
什么是流式細胞術?
流式細胞術:采用熒光素標記的單體克隆抗體及流式細胞儀檢測細胞抗原的表達、細胞大小、細胞內顆粒的多少,通過細胞表面結合的不同熒光標記的單克隆抗體將細胞分類。白細胞是人體與疾病斗爭的“免疫衛士”,其中淋巴細胞是機體細胞免疫和體液免疫應答功能的重要細胞成分,利用流式細胞術分析淋巴細胞亞群水平,可以幫助評價機體目前的免疫狀態,是目前廣泛應用于臨床各領域的重要檢測指標。
流式細胞術——免疫細胞評估
什么是腫瘤免疫力評估?
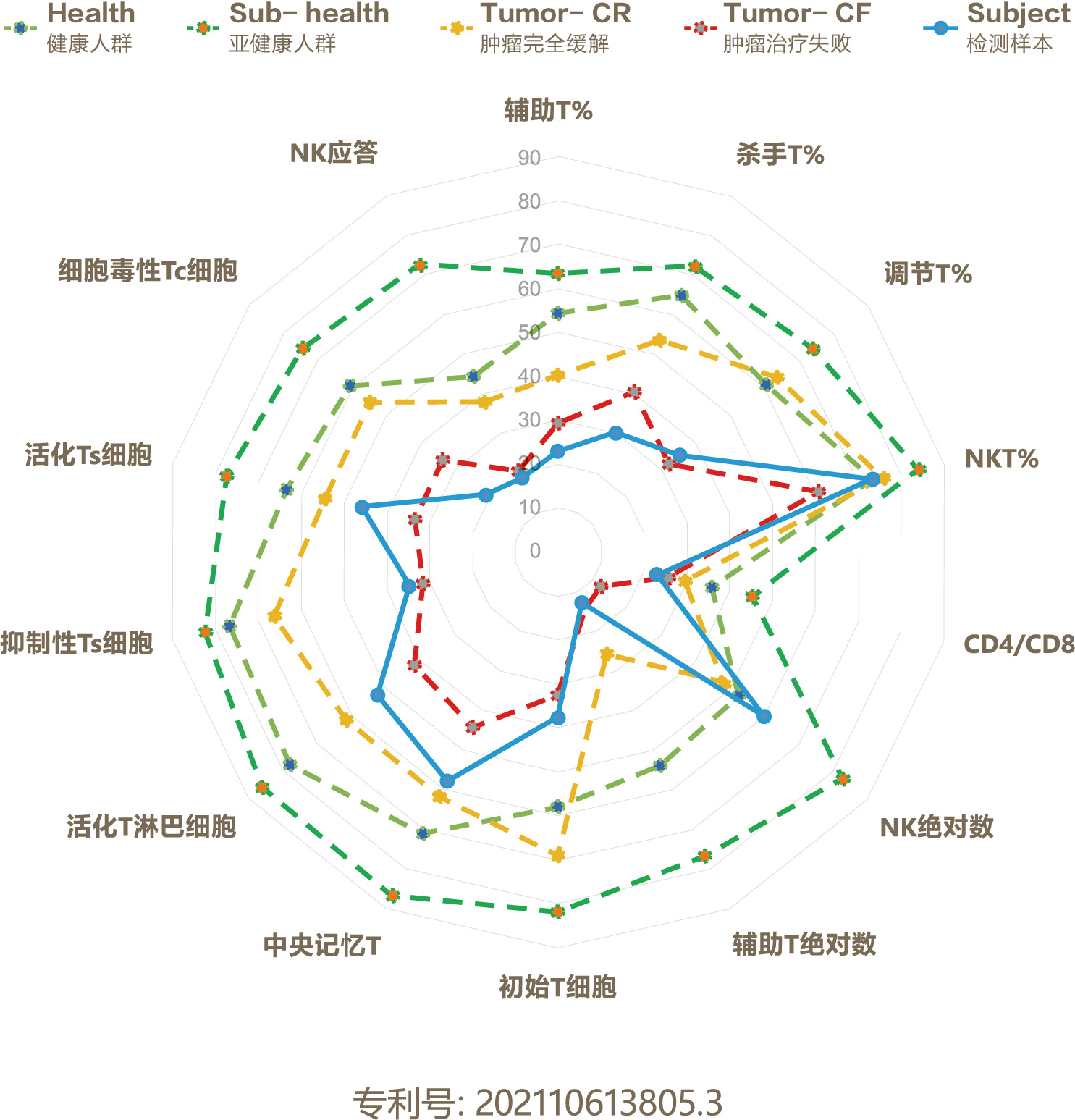
免疫細胞是人體與疾病斗爭的“免疫衛士”。免疫細胞評估是利用流式細胞術從數量、結構、功能等不同角度深入分析淋巴細胞的水平,進而對機體抗感染、抗腫瘤等免疫狀態作出精準評估,是目前廣泛應用于臨床各領域的重要檢測方式之一。
全方位監測“國防系統”,量化腫瘤免疫力
定期檢測,在上游發現并解決問題,避免進展至腫瘤
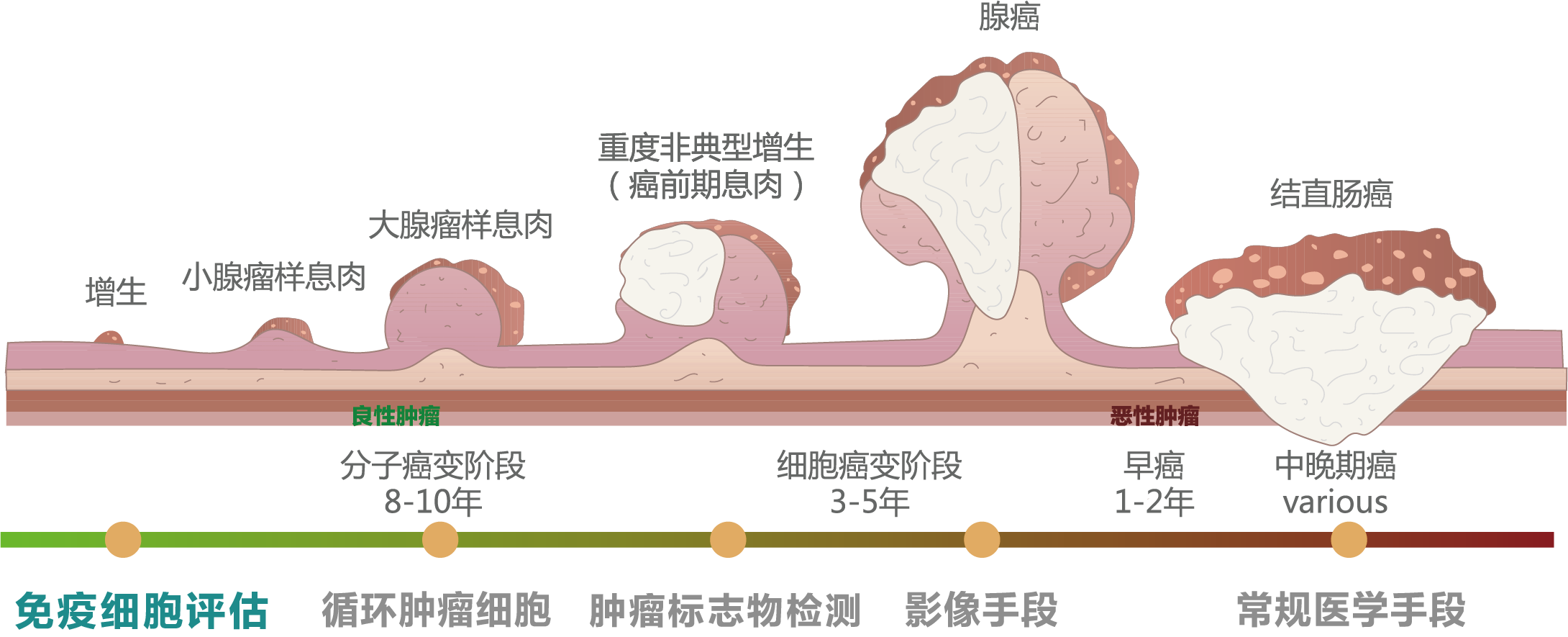
免疫細胞評估示意圖
流式細胞術——TILs細胞評估
什么是TILs細胞評估?
腫瘤浸潤淋巴細胞(tumor infiltrating lymphocyte,TIL)是指那些離開血流進入到腫瘤中的白細胞。當存在大量的腫瘤浸潤淋巴細胞時,表明機體啟動了對抗腫瘤的免疫反應。在許多的癌癥中,研究人員均開展了相關的研究,定量這些腫瘤浸潤細胞,并將其數量與腫瘤特征和結果關聯起來。
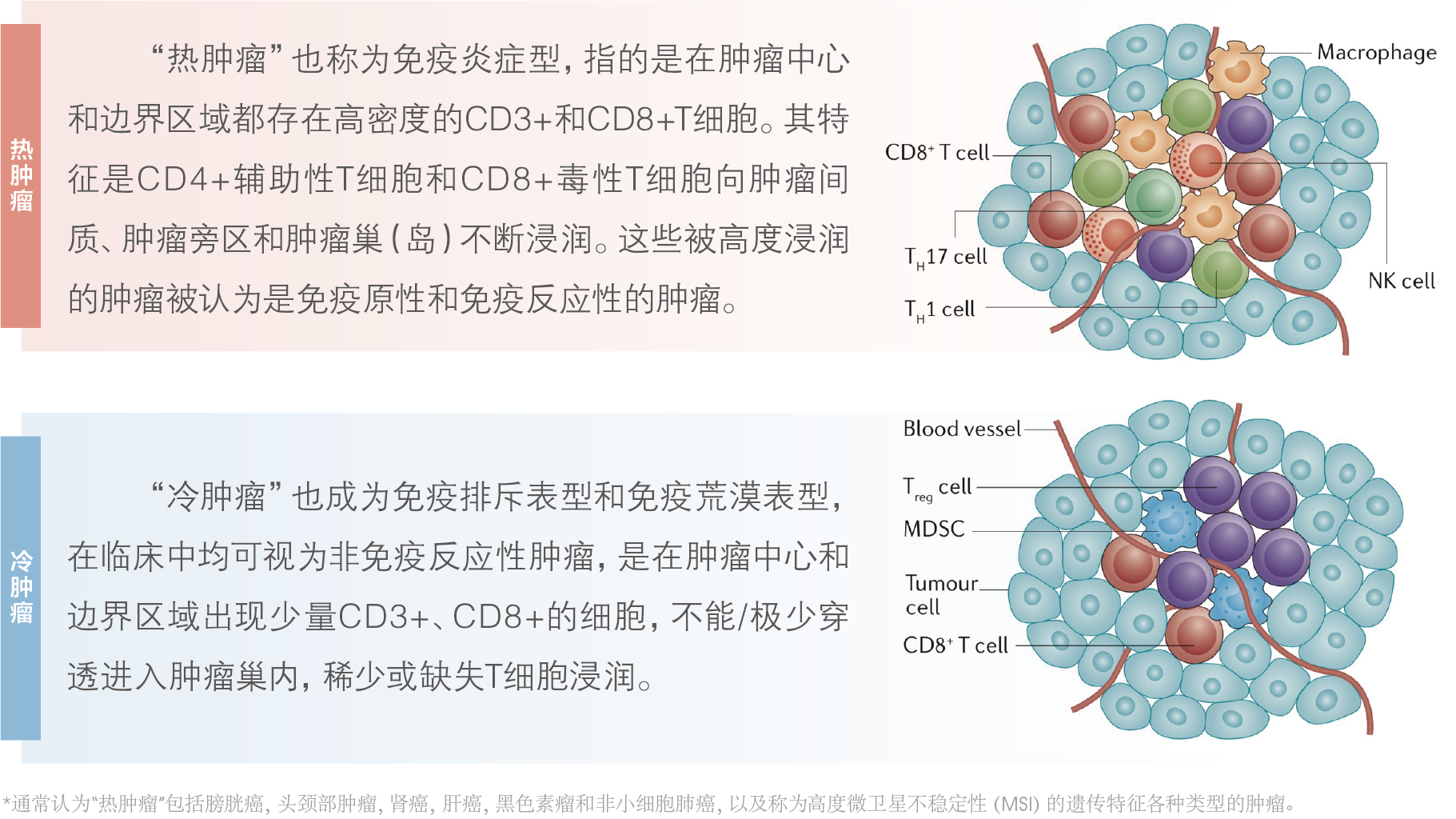
腫瘤組織分為熱腫瘤和冷腫瘤,熱腫瘤更容易通過免疫治療的方法獲益。
什么是熱腫瘤、冷腫瘤?
實體腫瘤免疫治療技術
TILs 、γδ T 、CRP-T(chimeric reverse PD1 signal-T cells)、NKT
熱腫瘤——應用免疫治療可能受益,對抗PD-1和抗PD-L1的免疫檢查點抑制劑(ICIs)治療響應效果好
冷腫瘤——提示可能缺乏或很少產生功能有效的腫瘤特異性T細胞,從而導致抗腫瘤免疫力的不足。冷腫瘤很少對抗PD-1和抗PD-L1的免疫檢查點抑制劑(ICIs)有響應。

參考文獻
[1]Nagarsheth N, Wicha MS, Zou W. Chemokines in the cancer microenvironment and their relevance in cancer immunotherapy. Nat Rev Immunol. 2017 Sep;17(9):559-572.
[2]Li J , Byrne K T , Yan F , et al. Tumor Cell-Intrinsic Factors Underlie Heterogeneity of Immune Cell Infiltration and Response to Immunotherapy[J]. Immunity, 2018:S1074761318302619-.
[3]Ochoa de Olza, M., et al., Turning up the heat on non-immunoreactive tumours: opportunities for clinical development. The Lancet Oncology, 2020. 21(9): p. e419-e430.
[4]Kuang DM, et al. Tumor-activated monocytes promote expansion of IL-17-producing CD8+ T cells in hepatocellular carcinoma patients. J Immunol. 2010; 185:1544–1549. [PubMed: 20581151]
[5]Wang W, et al. Effector T cells abrogate stroma-mediated chemoresistance in ovarian cancer. Cell. 2016; 165:1092–1105. [PubMed: 27133165]
[6]Bindea, G. et al. Spatiotemporal dynamics of intratumoral immune cells reveal the immune landscape in human cancer. Immunity39782-795(2013)
[7]Wieland,A.et al. T cell receptor sequencing of activated CD8 T cells in the blood identifes tumor infltrating clones that expand after PD-1 therapy and radiation in a melanoma patient. Cancer Immunol. Immunother67,1767-1776(2018).
[8]Wolchok,J.D.et al. Overall survival with combined nivolumab and ipilimumab in advanced melanomaNEnglJMed3771345-1356(2017). Motzer, R. J.et al. Nivolumab plus ipilimumab versus sunitinib in advanced renal-cell carcinoma.N.Engl.J.Med3781277-1290(2018).
[9]Hellmann, M. D.et al. Nivolumab plus ipilimumab in lung cancer with a high tumor mutational burden.NEngl JMed3782093-2104(2018).
上一篇:牙髓干細胞外泌體—骨關節炎
下一篇:沒有了!